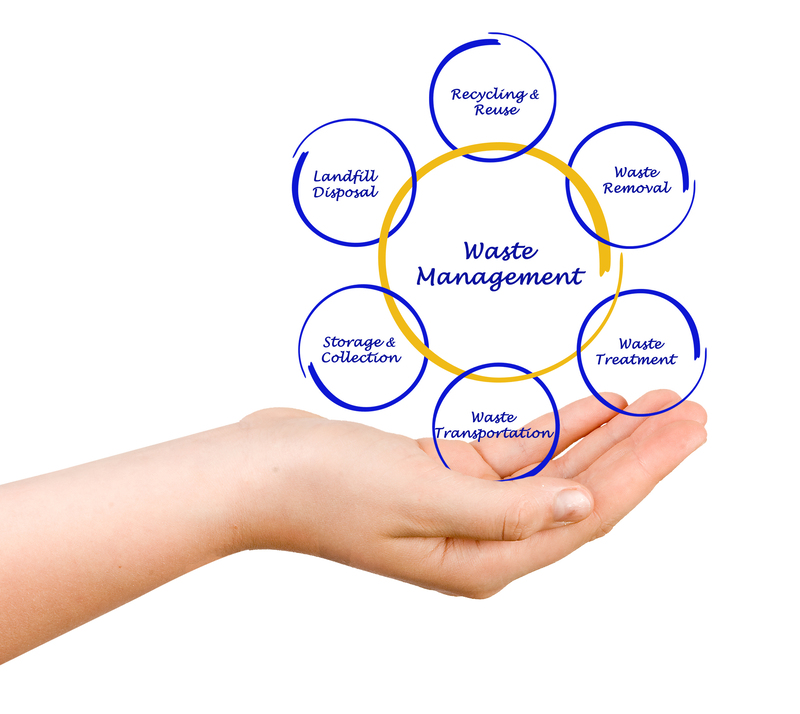
Waste Removal: A Comprehensive Overview
In today's fast‐paced world, waste removal has evolved into an essential service that supports clean communities, protected ecosystems, and sustainable industry practices. From urban centers to rural areas, the need for efficient waste disposal is paramount. This article delves into the multifaceted realm of waste removal, exploring its historical progression and modern-day iterations. Waste disposal methods now span a broad spectrum, including traditional garbage removal, innovative recycling, and state‐of‐the-art technological solutions that streamline the extraction of trash from residential, commercial, and industrial sites. The transformation of this service over recent decades has been influenced by increasing environmental awareness, government regulations, and technological breakthroughs. With a specific focus on the benefits and challenges of managing waste, this discussion provides an in‐depth understanding for community members, business owners, and policy makers alike.Modern trash removal services are not merely about collecting refuse—they represent a significant component of urban infrastructure and public health. As cities expand and populations surge, the efficiency of waste removal systems becomes even more critical. Municipalities have started integrating smart technologies with waste management operations to optimize collection routes, reduce fuel consumption, and minimize the environmental footprint. In parallel, private companies are innovating rapidly, adopting greener methods of waste disposal and recovery. The strategies now focus on reducing landfill waste and promoting recycling and energy recovery. This shift to sustainable waste disposal practices highlights the growing relationship between environmental stewardship and industry demands.
 In addition, rural regions have also witnessed an evolution in waste management services. The challenge in these less densely populated areas often lies in logistical efficiency and profitability. However, even in sparsely populated regions, there is an emerging trend toward modernizing waste removal services. Solutions include community‐oriented programs and collaborative partnerships that aim to reduce the accumulation of waste and foster local recycling initiatives. The sector now encompasses a wide range of services, from conventional garbage removal to specialized industrial waste disposal, underlining the importance of tailored approaches for diverse waste streams. With clear regulatory frameworks and heightened public demand for transparency, waste removal has become a significant driver of both economic development and environmental preservation.
In addition, rural regions have also witnessed an evolution in waste management services. The challenge in these less densely populated areas often lies in logistical efficiency and profitability. However, even in sparsely populated regions, there is an emerging trend toward modernizing waste removal services. Solutions include community‐oriented programs and collaborative partnerships that aim to reduce the accumulation of waste and foster local recycling initiatives. The sector now encompasses a wide range of services, from conventional garbage removal to specialized industrial waste disposal, underlining the importance of tailored approaches for diverse waste streams. With clear regulatory frameworks and heightened public demand for transparency, waste removal has become a significant driver of both economic development and environmental preservation.
Tracing the history of waste removal, one can observe a fascinating transition from rudimentary systems to sophisticated, eco‐friendly techniques. In ancient civilizations, refuse was often discarded without a second thought, sometimes even used as fertilizer in nearby fields. Over time, as the connection between waste and public health became apparent, early cities started devising systematic methods for waste collection. By the industrial era, the challenges of rapidly expanding urban centers required innovative solutions. Today, waste removal services combine the best of old practices and novel technologies to meet modern demands. Cities worldwide now follow strict guidelines to ensure garbage removal services not only protect public health but also promote recycling and energy recovery.
Eco‐friendly disposal methods are central to modern waste management. Businesses, municipalities, and non‐profit organizations now collaborate to reduce the environmental impact of trash removal. Sustainability has become a core driver in designing waste disposal systems, as more communities seek to lower their carbon footprint. Innovative techniques include biodegradable collection bags, automated sorting at recycling facilities, and clean energy generators fueled by processed waste. Such advancements in trash removal demonstrate that a commitment to environmental responsibility can coexist with efficiency and economic viability. Garbage removal processes have thus shifted from mere collection to effective management, promoting a zero‐waste lifestyle in many parts of the world.
In exploring the practical methods used by modern waste removal companies, one can appreciate a blend of technology and traditional service excellence.  Modern waste disposal techniques incorporate advanced routing software to optimize collection times, machinery designed for heavy lifting, and systems for sorting and recycling various waste streams. The procedures are often enhanced by feedback loops that help companies continually adjust to community needs and environmental targets. Furthermore, many organizations have implemented detailed quality control measures that include safety protocols and regular audits, ensuring that each collected item is processed in a manner that is both safe and sustainable. A sample of the many innovative practices includes:
Modern waste disposal techniques incorporate advanced routing software to optimize collection times, machinery designed for heavy lifting, and systems for sorting and recycling various waste streams. The procedures are often enhanced by feedback loops that help companies continually adjust to community needs and environmental targets. Furthermore, many organizations have implemented detailed quality control measures that include safety protocols and regular audits, ensuring that each collected item is processed in a manner that is both safe and sustainable. A sample of the many innovative practices includes:
- Automated sorting systems that help segregate recyclables from residual waste.
- Energy recovery programs that convert waste into usable power.
- Digital route optimization to reduce fuel consumption and limit greenhouse gas emissions.
Contemporary waste removal practices have revolutionized the way communities and industries handle their trash. Ongoing investments in research and development continue to lead to further innovations. Many modern companies now utilize sophisticated machinery capable of handling diverse forms of waste—from bulky residential artifacts to hazardous industrial materials. The integration of robotics and sensor technologies in waste removal tasks not only improves safety standards but also ensures a higher degree of sorting accuracy that can reduce recycling contamination levels. This progressive approach is crucial as modern waste streams become increasingly complex and varied.
Several challenges still persist despite the strides made in the waste removal field. Rapid urbanization, fluctuating economic conditions, and high volumes of municipal waste require constant adjustments to the methods and technologies used in waste disposal. For instance, while the implementation of automated systems has reduced the need for manual labor and minimized human exposure to hazardous materials, it has also introduced new challenges related to maintenance and programming. Authorities and waste removal companies are therefore required to invest not only in technological upgrades but also in ongoing training and skill development. Such adaptive strategies are key to ensuring that both waste removal services and the related regulatory frameworks can keep pace with rapid changes in urban and industrial waste generation.
Significant progress has also been made in ensuring that waste management procedures are both economically sustainable and socially responsible. The modern approach to garbage removal now involves engaging community members through recycling initiatives and awareness campaigns. Industries are pushed to rethink their production methods, emphasizing closed-loop systems that facilitate the reuse and recycling of materials rather than their disposal in landfills. Policy makers and environmental advocates continue to support programs that aim to reduce the overall volume of waste, turning potential pollution into opportunities for renewable energy production and sustainable resource recovery. This integrated method not only enhances the efficiency of waste removal but also contributes to long-term economic and environmental stability.
 The economic and social facets of waste removal form another critical area of discussion. Waste management is not simply about disposing of trash; it has considerable implications for local economies. The emergence of green technology and sustainable practices has created a dynamic market for innovative waste management solutions. In many regions, waste removal companies are now key job providers, supporting everything from high-tech machinery production to local recycling centers. Moreover, community-based initiatives have helped in establishing recycling hubs where residents and businesses actively participate in managing their own waste. These systems underline the growing role of waste disposal as a catalyst for economic growth and community empowerment, as well as environmental sustainability.
The economic and social facets of waste removal form another critical area of discussion. Waste management is not simply about disposing of trash; it has considerable implications for local economies. The emergence of green technology and sustainable practices has created a dynamic market for innovative waste management solutions. In many regions, waste removal companies are now key job providers, supporting everything from high-tech machinery production to local recycling centers. Moreover, community-based initiatives have helped in establishing recycling hubs where residents and businesses actively participate in managing their own waste. These systems underline the growing role of waste disposal as a catalyst for economic growth and community empowerment, as well as environmental sustainability.
In many communities, the integration of educational programs into waste removal strategies has led to a better-informed public that appreciates the importance of responsible waste management. Partnerships between local governments, waste removal companies, and community leaders have resulted in outreach programs and workshops that educate residents on best practices for waste segregation, recycling, and sustainable disposal. These educational initiatives are designed to promote transparency and cooperation, ensuring that everyone from businesses to individual households understands their role in preserving the environment. By emphasizing real‐world benefits and highlighting success stories from various cities, waste removal initiatives become more relatable and encourage broader community participation.
 In conclusion, effective waste removal is pivotal for maintaining a thriving, sustainable environment. The evolution of waste disposal strategies over time—from traditional trash pick-up methods to modern, technologically advanced waste management systems—reflects a growing recognition of the value of environmental conservation and public health. As research pushes the boundaries of what is possible, future waste removal operations are expected to harness even more sophisticated techniques. These include innovations like AI-assisted collection services, automated sorting lines with higher throughput capacities, and new recycling methods that recover valuable materials from what was once deemed worthless. Embracing a holistic approach that blends economic prudence, technological advances, and community engagement, the future of waste removal appears bright and full of promise. This thorough understanding of trash removal, including industrial, residential, and specialized waste disposal, empowers societies to reduce environmental hazards and create resilient, eco-friendly communities.
In conclusion, effective waste removal is pivotal for maintaining a thriving, sustainable environment. The evolution of waste disposal strategies over time—from traditional trash pick-up methods to modern, technologically advanced waste management systems—reflects a growing recognition of the value of environmental conservation and public health. As research pushes the boundaries of what is possible, future waste removal operations are expected to harness even more sophisticated techniques. These include innovations like AI-assisted collection services, automated sorting lines with higher throughput capacities, and new recycling methods that recover valuable materials from what was once deemed worthless. Embracing a holistic approach that blends economic prudence, technological advances, and community engagement, the future of waste removal appears bright and full of promise. This thorough understanding of trash removal, including industrial, residential, and specialized waste disposal, empowers societies to reduce environmental hazards and create resilient, eco-friendly communities.